In today’s world, sustainability is no longer a niche concept; it’s a business imperative. Consumers, employees, and investors are increasingly demanding that companies demonstrate a commitment to environmental and social responsibility. One of the most impactful ways businesses can embrace sustainability is through their physical spaces. Sustainable interior design goes beyond simply using “green” materials; it’s a holistic approach to creating commercial spaces that are environmentally responsible, healthy for occupants, and economically beneficial.
The Importance and Benefits of Sustainable Interior Design
Sustainable interior design offers a triple bottom line benefit:
- Environmental Benefits: Reduced carbon footprint, lower energy consumption, minimized waste, conservation of natural resources, and improved air quality.
- Economic Benefits: Lower utility bills through energy efficiency, reduced material costs (through reuse and recycling), increased property value, and potential tax incentives.
- Social Benefits: Improved employee well-being, increased productivity, enhanced brand reputation, attracting and retaining talent, and creating a positive work environment.
Key Principles of Sustainable Interior Design
Here are the core aspects to consider, along with actionable steps.
- Choosing Eco-Friendly Materials and Finishes:
- Prioritize Recycled Content: Opt for materials made from recycled content, such as recycled glass countertops, reclaimed wood flooring, and recycled plastic furniture.
- Choose Renewable Resources: Select materials that are rapidly renewable, such as bamboo, cork, and linoleum.
- Select Low-VOC Products: Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) are harmful chemicals emitted from many conventional building materials and finishes. Choose low-VOC or zero-VOC paints, adhesives, sealants, and flooring to improve indoor air quality.
- Consider Material Lifecycles: Evaluate the entire lifecycle of a material, from extraction and manufacturing to transportation, use, and disposal. Choose materials with minimal environmental impact throughout their lifecycle.
- Source Locally: Cut down on transportation costs and pollution.
- Maximizing Energy Efficiency:
- Optimize Natural Light: Maximize the use of natural light through strategic window placement, skylights, and light shelves.
- Implement Efficient Lighting Systems: Use LED lighting, which consumes significantly less energy than traditional incandescent or fluorescent lighting. Incorporate lighting controls like dimmers, timers, and occupancy sensors.
- Upgrade HVAC Systems: Invest in energy-efficient heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems. Consider smart thermostats and building automation systems to optimize energy use.
- Improve Insulation: Proper insulation reduces heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer, lowering energy consumption.
- Implementing Waste Reduction and Recycling Practices:
- Design for Deconstruction: Consider how materials can be easily disassembled and reused or recycled at the end of their life.
- Minimize Construction Waste: Carefully plan material orders to avoid excess waste. Work with contractors who prioritize waste reduction and recycling.
- Implement Recycling Programs: Provide clearly labeled recycling bins throughout the workspace.
- Choose Reusable and Durable Furniture: Invest in high-quality, durable furniture that can withstand heavy use and is designed for longevity.
- Improving Indoor Air Quality:
- Ensure Proper Ventilation: Provide adequate ventilation to remove pollutants and bring in fresh air.
- Use Low-VOC Materials: As mentioned earlier, choosing low-VOC products is crucial for maintaining healthy indoor air quality.
- Incorporate Air-Purifying Plants: Certain plants can help filter out indoor air pollutants and improve air quality.
- Regular HVAC Maintenance: Schedule regular maintenance of HVAC systems to ensure they are operating efficiently and not contributing to indoor air pollution.
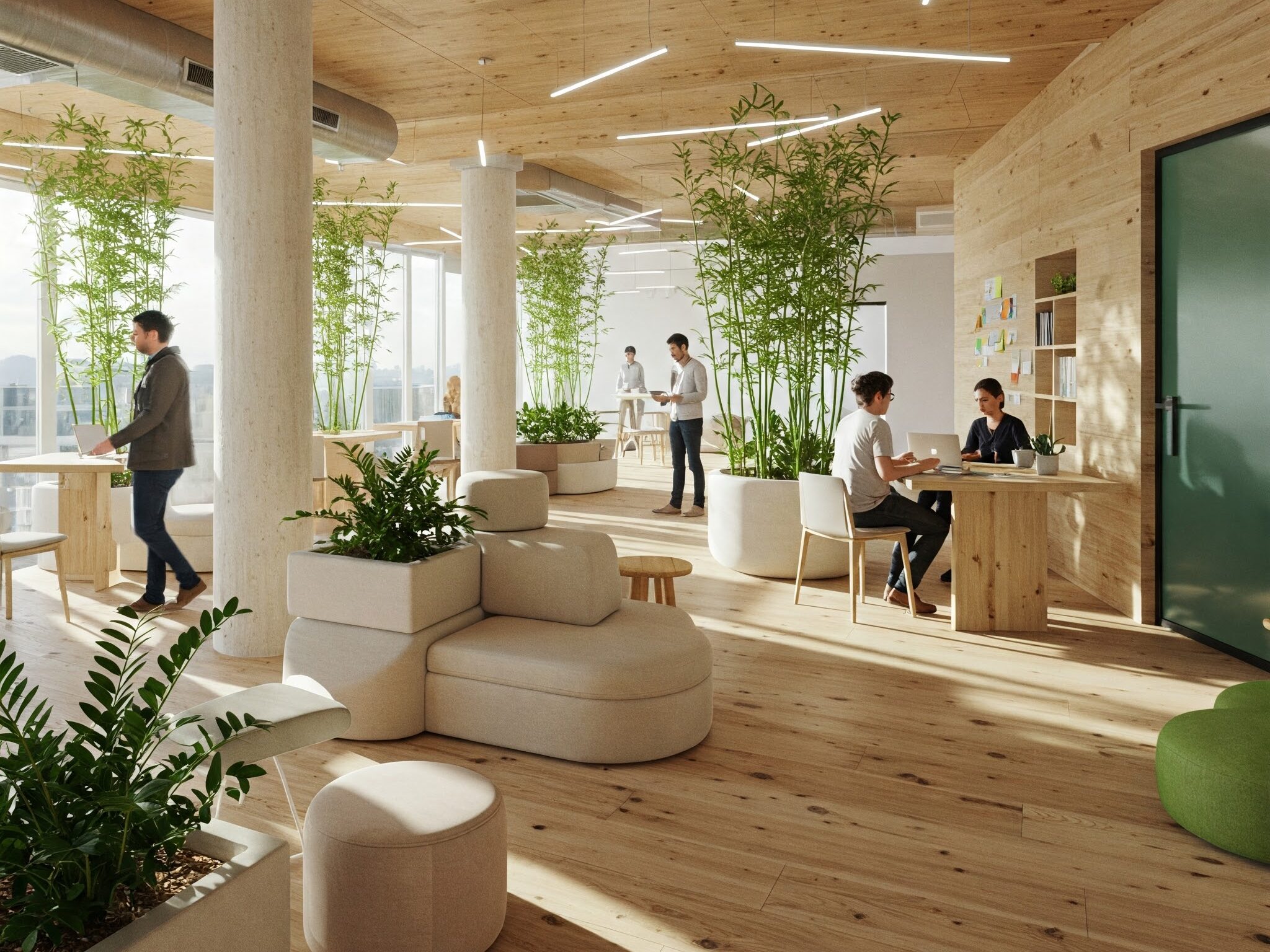
- Integrating Biophilic Design Principles:
- Maximize Natural Light: As discussed earlier, natural light is crucial for biophilic design.
- Incorporate Natural Elements: Use natural materials like wood, stone, and water features to create a connection to nature.
- Provide Views of Nature: If possible, provide views of outdoor greenery or natural landscapes.
- Use Natural Patterns and Forms: Incorporate patterns and forms found in nature into the design, such as curves, spirals, and textures.
- Add plants. Plants improve air quality, reduce stress, and enhance the overall aesthetic.
- The Role of Technology in Sustainability:
- Smart Building Systems: Implement smart building systems to monitor and control energy use, lighting, and HVAC systems.
- Energy Monitoring Tools: Use energy monitoring tools to track energy consumption and identify areas for improvement.
- Automated Lighting Controls: Utilize sensors and timers to automatically adjust lighting levels based on occupancy and natural light availability.
- Understanding Sustainable Design Certifications:
Certifications like LEED, WELL, and BREEAM offer recognizable standards for sustainable practices.
- LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design): A globally recognized green building rating system.
- WELL Building Standard: Focuses on the health and well-being of building occupants.
- BREEAM (Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method): A sustainability assessment method for buildings.
Achieving certification can demonstrate a company’s commitment to sustainability and provide a framework for achieving specific sustainability goals.
Practical Steps for Businesses
- Assess Your Current Space: Conduct an audit of your existing space to identify areas for improvement in terms of energy efficiency, waste reduction, and indoor air quality.
- Set Sustainability Goals: Define specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals for your sustainable design project.
- Develop a Budget: Determine a realistic budget for your project, considering both upfront costs and long-term savings.
- Choose the Right Design Partners: Work with architects, interior designers, and contractors who have experience in sustainable design.
- Educate Employees: Involve employees in the process and educate them about the benefits of sustainable design.
- Monitor and Measure Results: Track your progress and measure the impact of your sustainable design initiatives.
Conclusion: Partnering for a Sustainable Future
Sustainable interior design is no longer a trend; it’s a responsible and beneficial approach to creating commercial spaces. By embracing these principles, businesses can reduce their environmental impact, create healthier and more productive workspaces, and enhance their brand reputation. DIG Interior Design Solutions is committed to helping businesses achieve their sustainability goals.
Our team of experienced designers can guide you through every step of the process, from initial assessment to implementation, creating a space that is both beautiful and environmentally responsible. Contact us today to learn more about how we can help you create a sustainable future for your business.